Many local and diaspora organisations are opposing Esencia, a luxury tourism and residential megaproject with a private airport, in Cabo Rojo. The development has been granted generous tax credits and would require vast volumes of water.
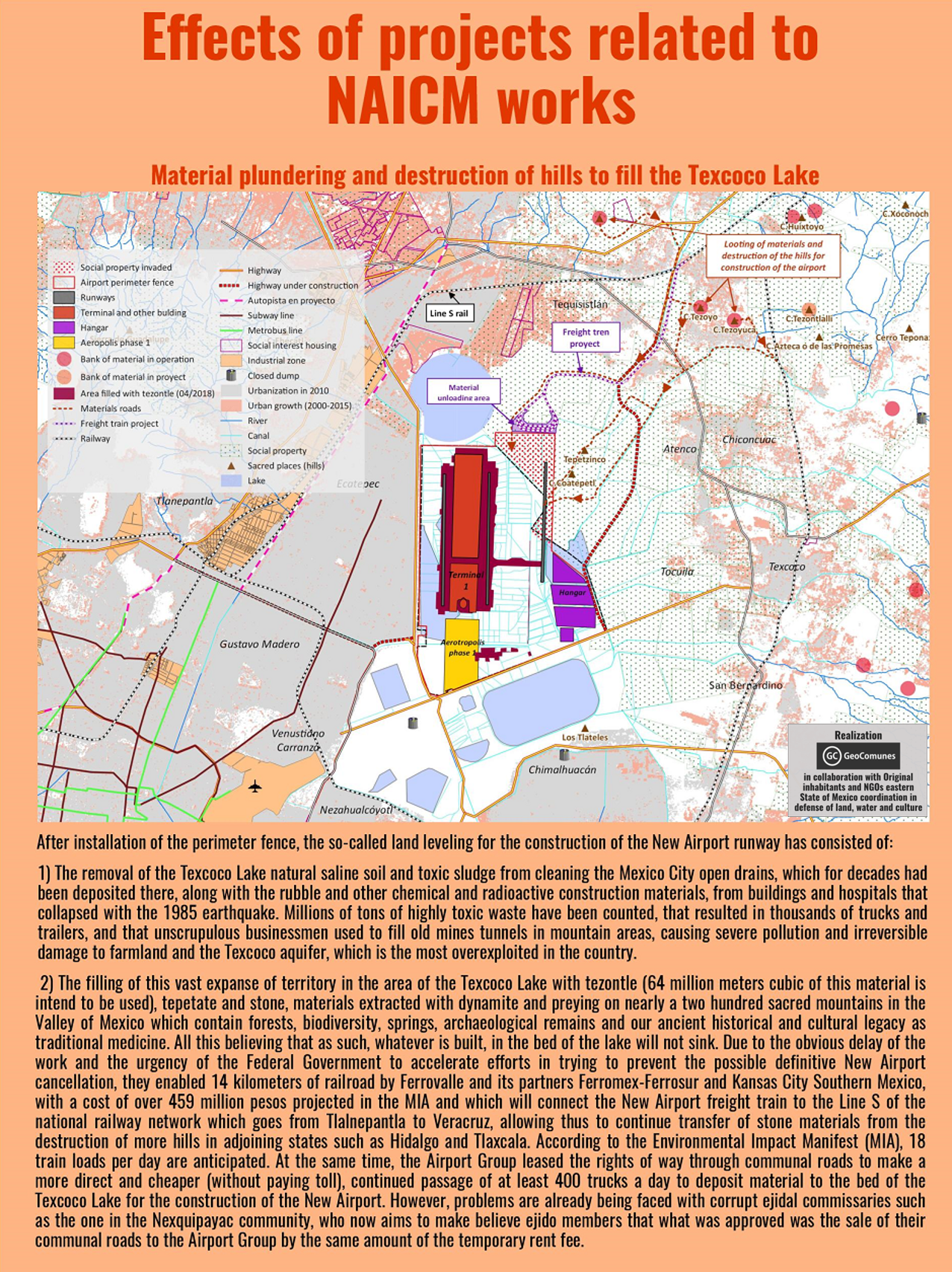
In May 2024 two real estate firms, Reuben Brothers and Three Rules Capital, filed a master plan for Esencia, a USD2billion development in Boquerón Bay, Cabo Rojo on the west coast of Puerto Rico. Anchored by international hotel operators Mandarin Oriental Hotel Group, Aman Group and Rosewood Hotels and Resorts and containing up to 500 luxury hotel rooms and 900 tourist residences the complex would have a private airport. The Esencia website says the new ‘residential and hospitality community’ will have 3 miles (4.8km) of ‘pristine beachfront’. Plans also included two golf courses, spa, wellnesses centre, health clubs, equestrian centre, hiking and biking trails and a school.

The Esencia project was granted more than USD497 million in tax credits and in August 2024 four new tax exemptions of between 90 and 100 per cent were approved. A new decree granting 100 per cent fuel tax exemption for tourism-related activities was criticised for incentivising high levels of fossil fuel usage. Comité por la Verdadera Esencia del Suroeste sent statements to multimedia platform Marea Ecologista concerning the proximity of the project site to protected ecologically sensitive areas providing habitats for endangered birds such as the Puerto Rican nightjar. Responding to the absence of public hearings on permits and boundary demarcation for the Esencia project a town hall was convened by local community, environmental and cultural groups on 28th September 2024 where further detail of Esencia project components, including shopping malls and renovation of an airstrip to accommodate small aircraft, was shared.
The land within the site is rural and falls under two classifications. One category is rural land protected because of its ecological importance as it is located between two nature reserves and serves as a corridor for many species and also for its recreational value. The second category is rural land where there is more flexibility regarding development and in recent years mechanisms to evade compliance with the land use plan have been deployed such as declaring projects to be strategic or of critical importance. The project area contains at least 24 archaeological sites from the colonial and pre-colonial eras, many of which have not yet been explored.
On the first day of public hearings in March 2025 Cabo Rojo’s streets were filled with protesters holding posters and banners, many declaring ‘No to Esencia’ and calling the project an enclave for a small number of billionaires. The hall was not big enough to accommodate all the people opposing the project so many watched the proceedings on a screen in a tent outside. Puerto Rican groups opposing the project joined forces under the slogans ‘Defend Cabo Rojo’ and ‘No to Esencia’. The anti-Esencia movement gained support from Puerto Rican diaspora and pro-independence organisations, amplifying locals’ calls for cancellation of the project and holding protests throughout New York. For example, protesters occupied the lobby of the Mandarin Oriental Hotel and unfurled banners in the luxurious Columbus Circle shopping mall.
Officials said the project’s environmental impact statement (EIS) did not address the impacts on infrastructure and ecosystems and lacked hydrological studies. Esencia would place additional strain on water supplies, consuming more than 1.25 million gallons per day, a volume equal to more than a third of current consumption in the Cabo Rojo Municipality. This is a low estimate as it does not include the project proposal’s two golf courses which would increase the volume of water consumed per day to 2 million gallons. The development would require extraction from aquifers or connection to the existing drinking water system but neither of these options are feasible. Local fishers expressed concerns over the risk of damage to oyster beds and disruption of freshwater and saltwater flows that are essential to the health of the estuarine environment.
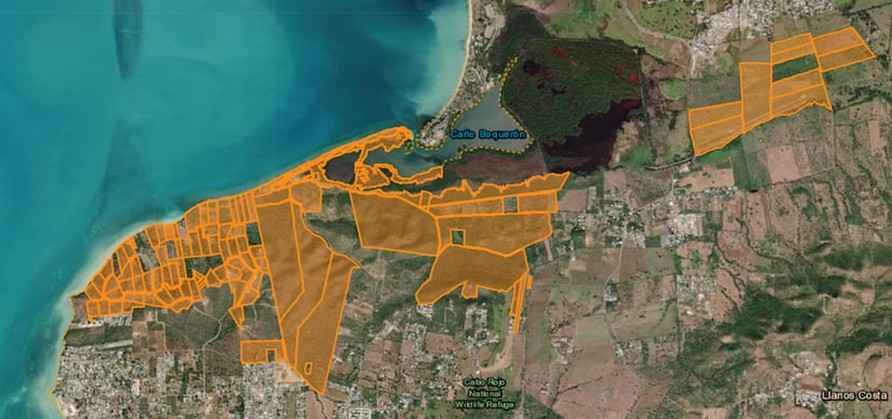
By September 2025 project investors had spent approximately USD147 million on properties for Esencia and were on track to acquire the target of 809 hectares of land. Recent land parcel purchases were part of the Reserva Agrícola del Valle de Lajas (Lajas Valley Agricultural Reserve) and an airstrip. On 12th September the Department of Natural and Environmental Resources (DNRA) published a 29-page report firmly reiterating its opposition to the Esencia project and concluding that the plans did not comply with environmental laws. Significant findings included fragmentation of habitats hosting endangered bird species, severe impacts on Catesbaea melanocarpa, a rare, endangered lily and threats to the habitat of Anolis poncensis, a rare lizard species. The project’s so-called ‘ecological corridors’ lacked the connectivity of existing ecosystems and golf courses, artificial ponds and landscaping claimed to be mitigations would be part of the project’s negative impacts.
For more information including references for all source material and photos see the case study on EJAtlas, the world’s largest, most comprehensive online database of social conflict around environmental issues – Esencia project, Puerto Rico
By 3rd November 2025 a petition – STOP THE LUXURY MEGAPROJECT “ESENCIA” IN CABO ROJO, PUERTO RICO NOW – calling on the Puerto Rican government and its agencies to stop the permit granting process, protect the land, study submitted material and conduct a transparent investigation prioritizing affected communities and experts, had attracted 36,327 signatures: Detengan ahora el megaproyecto de lujo “Esencia” en Cabo Rojo, Puerto Rico (STOP THE LUXURY MEGAPROJECT “ESENCIA” IN CABO ROJO, PUERTO RICO NOW)