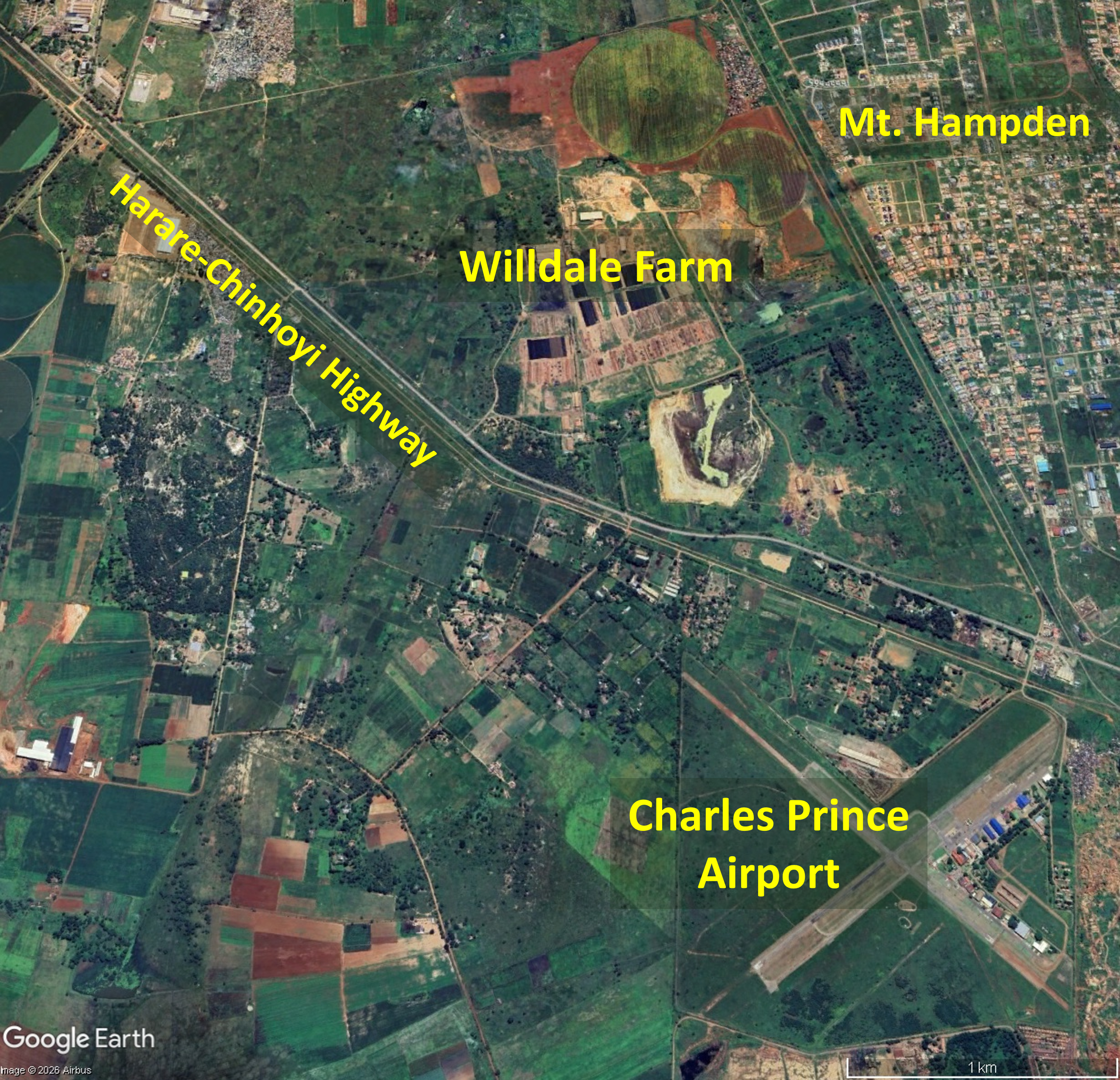
Forcible eviction of informal settlements from Willdale Farm, to make way for residential units, an industrial park and to support expansion of Charles Prince Airport, led to a humanitarian crisis. Over 7,000 people were left stranded by the roadside without shelter, food, water or sanitation.
In September 2025 more than 7,000 families residing on Willdale Farm, in the Mount Hampden area northwest of Harare, on land used for extracting clay for brick manifacturing, were served with eviction orders. Addressing the thousands of affected residents on 28th September Zimba East MP Kudakwashe Mananzva made reassurances that the government was committed to resettling all affected families and nobody would be rendered homeless. But people threatened with eviction complained that the landowner, brickmaking firm Willdale, was exerting pressure to force them to leave. On 29th November Zimbabwe Human Rights Association (ZimRights) reported that forced eviction had ’created an urgent protection crisis’. Evicted people had been left without shelter in heavy rains raising serious human rights concerns including rights to adequate housing and protection from inhumane treatment. On 2nd December New Zimbabwe reported that the ‘humanitarian crisis at Willdale Farm has deepened’; more than 7,000 residents had been evicted and were camped alongside the Harare-Chinhoyi highway to the south of Willdale Farm. The Department of Civil Protection acknowledged the scale of the eviction and said a temporary relocation site had been identified, about 14km northwest of Willdale Farm in Nyabira. State of the Nation reported widespread concerns over a ’humanitarian crisis’ affecting a vulnerable population including children and elderly people.
Zimbabwe Human Rights Commission (ZHRC) expressed serious concerns over the Willdale Farm mass eviction, flagging legal failings. On a 29th November site visit chairperson Jessie Majome saw hundreds of evicted people camped out along the road in the open air without water, sanitation or water. A 2nd December follow-up visit by the ZHRC secretariat confirmed that about 7,000 people including children, the elderly and disabled were still stranded. ZHRC said civil procedures had been violated, including the right to be heard, which might constitute a breach of constitutional rights pertaining to the right to a fair hearing and freedom from arbitrary eviction. ZHRC acknowledged efforts by the government to provide temporary alternative land in Nyabira but the relocation process was ‘extremely slow’, at this juncture nearly 8,000 people had been evicted but only 36 families had been relocated. A monitoring report by Zimbabwe Peace Project (ZPP) highlighted the Willdale Farm eviction, with families granted less than one hour to leave their homes before bulldozers arrived, as one of the most serious incidences of 123 human rights violations recorded in November 2025.
On 8th December Willdale announced that it had gained vacant possession of the 123.6314 hectares of land that had been occupied by third parties and the appointed contractor began mobilising equipment for construction of the project, an industrial park to support an emerging new city and expansion of Charles Prince Airport, located to the south of Willdale Farm and currently used by light aircraft and flights schools, into a regional hub for trade and commerce. An agreement for expansion and upgrade of Charles Prince Airport, was established between Zimbabwe and China during President Mnangagwa’s visit in 2024. Transport and Infrastructure Development Minister Felix Mhona highlighted the land and space for development around Charles Prince Airport, saying, “Once completed, the airport will serve as an international airport”, mentioning the airport’s proximity to the new Cyber City and new parliament building, located northeast of Willdale Farm. The Airports Company of Zimbabwe (ACZ) December 2025 announcement of airport infrastructure projects for the following five years highlighted upgrade of Charles Prince Airport, estimated to cost USD1 billion and supporting the government drive to establish new business and administrative hubs in the Mount Hampden area.
For more information including references for all source material, photos and videos see the case study on EJAtlas, the world’s largest, most comprehensive online database of social conflict around environmental issues – Willdale Farm mass eviction, Zimbabwe