Earthworks for construction of an airport on Koh Rong island, 25 km from the city of Sihanoukville on Cambodia’s south-west coast, began in January 2024. Satellite imagery shows the airport site, located in a flat area in the centre of the island. The new airport with a 2.650 metre runway will have capacity to handle 138,000 passengers annually upon completion of the first phase and the MoU signed in January 2023 formalised a budget of $300 million. The necessity and viability of Koh Rong International Eco-Tourism Airport seems questionable with two major international airports nearby. Newly constructed Dara Sakor Airport, with capacity for 10 million passengers per annum and scheduled to begin operations in November 2024, is only 21km away. Sihanouk Airport is 45 km away. Also, Koh Rong is already well served by boat; the ferry journey from Sihanoukville only takes about 45 minutes.
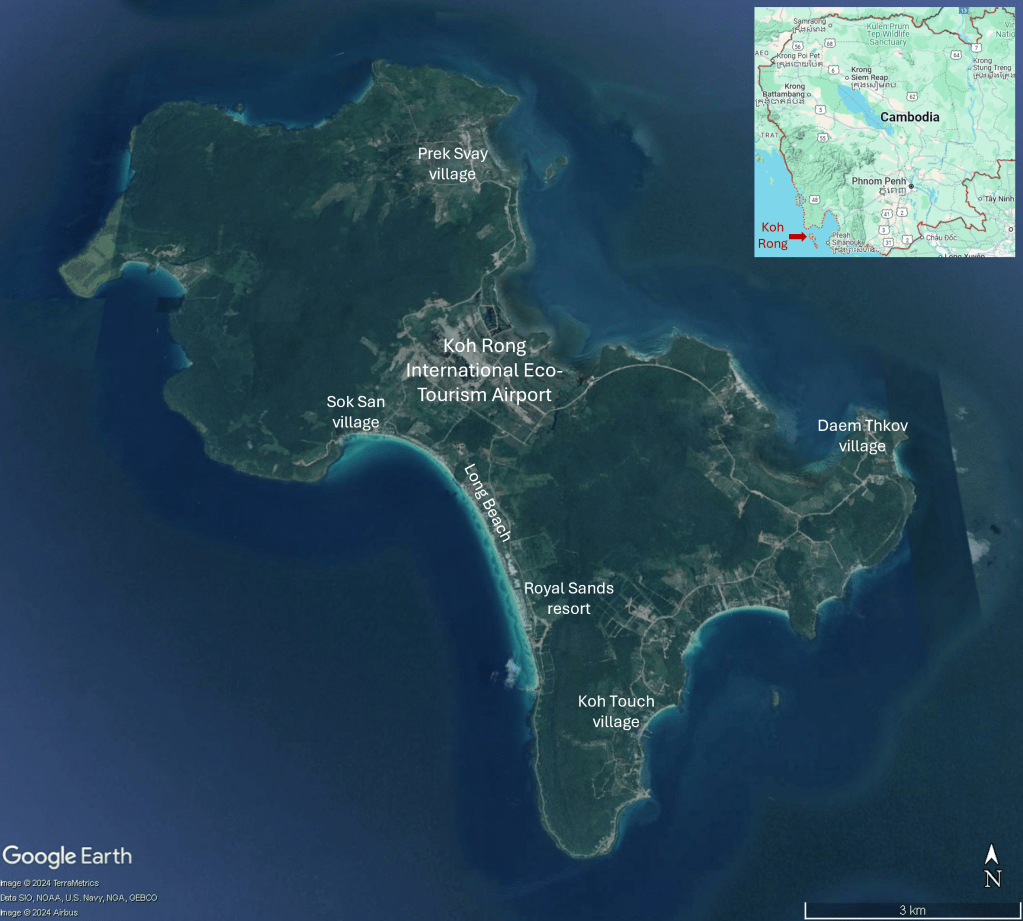
The new airport will be named ‘Koh Rong International Eco-Tourism Airport’. While an airport enables people to visit and explore protected beaches, forests and native wildlife habitats, it does the very opposite of protecting ecosystems, concreting over a vast area for runways, terminals and access roads. Then there is the issue of climate disrupting greenhouse gas emissions from flights, with aviation being energy intensive and dependent upon fossil fuels. And tourism development on Koh Rong has damaged ecosystems and the people depending on them. In 2008, Royal Group, one of the largest investment and development companies in Cambodia, was granted a 99-year land concession to develop the 78 square kilometre island. Realisation of the masterplan – featuring resorts, casinos, marinas, golf courses, two fishing villages and an airport – was delayed but commenced in 2015 with clearance of sites along the southwestern coast including forests along with construction of a road. On 3rd July 2015 Koh Touch villagers held a sit-in protest, blocking construction crews, excavators and a bulldozer, in response to construction of a road which they said would cut through their village and affect their homes. Later that month opposition to development of Koh Rong became more vocal in response to construction equipment and workers appearing on the island. Hundreds of residents began to speak out on social media. As well as cutting trees cliffs and rocky outcrops had been flattened for development, including a new pier on Long Beach, on the southeast of the island.
In August 2015 a number of Koh Kong residents called on officials to review what they called “abusive activities” by Royal Group. Construction had accelerated in recent weeks and workers and machinery had been photographed clearing large areas of forest. Residents accused Royal Group of destroying farmland and crops, including cashew, jackfruit, coconut and mango trees. A village leader said destruction could impact the livelihoods of over 100 families, who had lived on the island since 1995. Villagers said the destruction of their livelihoods was illegal and authorities should monitor the situation. Human rights and environmental campaigners supported residents’ calls for improved oversight and local groups were preparing petitions and other documents to file with provincial and national authorities. Protest groups had been formed in response to a breakdown in communications between residents and Royal Group. One villager said, “They come in and do their work, take whatever they want, but there is no communication”.
Controversy over land titles for Koh Rong villagers was reported in 2017. Some residents who had lived on the island since before 2008 had land titles, although it was uncertain whether these titles would be upheld amid disputes. Those arriving after 2008 did not have land titles. By 2018 over 1,000 land plots, belonging to 500 families, had been recognised by the government, but in April 2018, during the inauguration of the luxurious, five-star Royal Sands Koh Rong resort, about 50 people who had not yet received land titles attempted to join the event but were prohibited from doing so. Prime Minister Hun Sen ordered the Ministry of Land Management to bring an end to the Koh Rong land dispute. In June 2020 53 families protested land clearance; a 35-hectare site they believed rightfully belonged to them was being bulldozed. A Preah Sihanouk Provincial Administration spokesperson called on the protesting families to cooperate with authorities by providing relevant documents and warned them that if they caused chaos legal action would be taken against them. A member of one of the protesting families claimed they had lived in the area since 1992 and said: ”We won’t go anywhere. I will gather to protest at this site. We dare not enter the bulldozing site. I want Prime Minister Hun Sen to see and tackle this issue for us. We all have ownership documents.”
In June 2024 Mongabay reported that a new map of Royal Group’s plans for Koh Rong showed golf course zones, commercial zones, accommodation zones, casinos zones and an international airport. The latest plans did not appear to impact fishing villages but included clearing some of the Koh Rong’s protected forests to make way for golf courses. In total, project plans entail clearing more than 3,100 hectares of the island’s forests. A photo showed bulldozers and trucks working on the airport site. Sixteen years after the land was leased to Royal Group there was still no publicly available social or environmental impact assessment and islanders’ future was uncertain. Some Koh Rong residents hoped to sell their land to Royal Group while others feared that it would be taken from them.
For more information about the airport and tourism projects on Koh Rong island, including references for all source material, see the case study on EJAtlas, the world’s largest, most comprehensive online database of social conflict around environmental issues: Koh Rong island tourism development, Cambodia.